Location:
PMKI > Stakeholder
Management > Stakeholder Circle® Methodology-
Visualization.


- Stakeholder Circle®
Methodology Overview
- Stakeholder Visualization
- Articles & Papers - Stakeholder
Visualization
Other related sections of the PMKI:
- Stakeholder Circle
Help - Visualization
- Advanced Stakeholder
Engagement
- The Stakeholder Relationship
Management Maturity Model (SRMM®).
The Stakeholder Circle® has been designed to focus management attention on the stakeholders that are important at this point in time, to the success of the business activity, or project, they are managing. It incorporates a proven methodology supported by a robust, easy to use tool that guides you through five easy steps to:
 The
Stakeholder Work Sheet (SWS) is a sophisticated Excel
spreadsheet built to implement the Stakeholder Circle®
methodology - see
more on the SWS.
The
Stakeholder Work Sheet (SWS) is a sophisticated Excel
spreadsheet built to implement the Stakeholder Circle®
methodology - see
more on the SWS.
The third stage is visualizing the business unit's, or
project’s, important stakeholders using the Stakeholder
Circle.
See more on visualizing stakeholders using the Stakeholder
Circle SWS spreadsheet.
The top 15 stakeholders (based on their priority) are selected for display in the Stakeholder Circle. The diagram represents a symbolic stakeholder community, depicting the relative importance and direction of influence through color coding, and the size and placement of the segments within the circle. This diagram provides valuable pictorial information to assist in understanding the stakeholder community as at the time of its creation, which is the key to targeting the right stakeholders at the right time in the life of the activity and providing them with the right level of engagement, information and communication needed to enhance the probability of success.
The ranked list of all stakeholders is used to develop the communication plan.
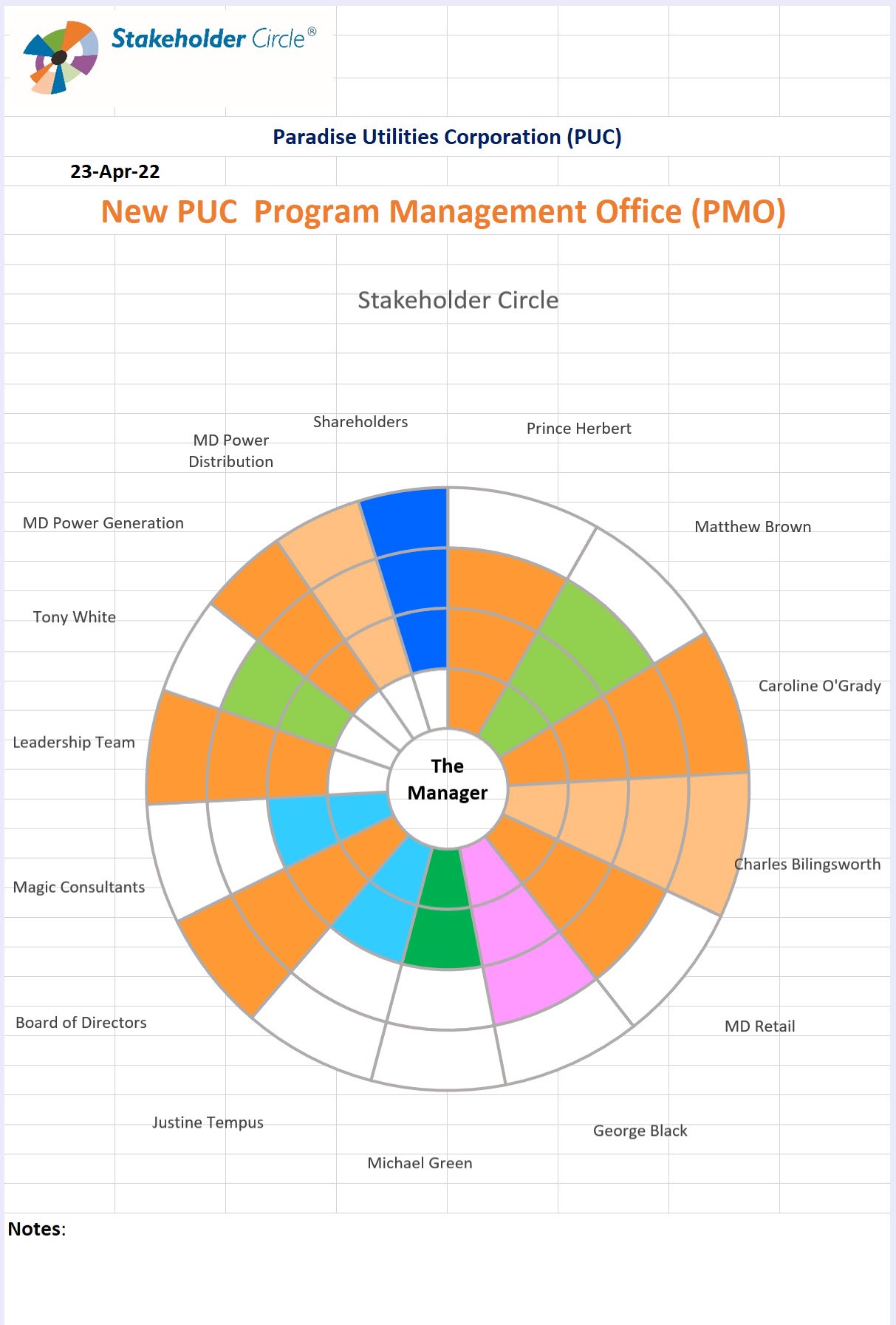
Download the Reading the Stakeholder Circle PDF.
See more on visualizing stakeholders using the Stakeholder Circle SWS spreadsheet.
Prs: Seeing who's there - A Brief History of Stakeholder Mapping & Visualization. Given project managers are required to identify and manage stakeholders (PMBOK® Guide 2008 onward) it is helpful to understand where the concept came from and what it represents, so as to ground decisions being made today, and anticipate likely stakeholder management demands in the future.This paper focuses on describing the evolution of the concept of stakeholders from the 1970s through to the present day and the closely allied visualization tools used at different times to see ‘who they are’. From this basis a current definition of stakeholders is determined and the merits of a range of current stakeholder management tools briefly described. The paper demonstrates that understanding ‘who’s there’ and more importantly ‘who matters’ is highly dependent on the tools and definitions used.
PP: Visualizing and Mapping Stakeholder Influence. This paper describes research that was conducted during 2004/2005 centred around the Stakeholder Circle tool. The Stakeholder Circle offers a useful and effective way to visualise stakeholder power and influence that may have pivotal impact on a project's success or failure. The Stakeholder Circle tool is developed for each project through a methodology that identifies and prioritises key project stakeholders and then develops an engagement strategy to build and maintain robust relationships with those key stakeholders.
 PP:
Visualizing Stakeholder Influence - Two Australian
Examples. This paper illustrates the use of
the Stakeholder Circle
as a tool for measuring and visualizing stakeholder
influence drawing upon two case study examples. It is
exploratory in nature and the case studies used provide a
useful vehicle for reflection and sense making.
Development of the Stakeholder
Circle was based upon stakeholder and
project management theory and it extends our appreciation
of the potential impact that stakeholders may exert that
unearths vital risk management and customer relationship
implications for the project management profession. Using
a case study and action learning approach, this paper
draws upon emerging project management and wider strands
of management decision-making literature. The results of
the analysis showed significant differences in the
processes needed to manage the respective groups. The
project teams recognized they needed to adopt
significantly different strategies to achieve stakeholder
engagement, leading to stakeholder satisfaction and a
successful project. The tool was found by the case study
respondents to be useful and that it also complements and
enhances risk management approaches.The Stakeholder
Circle can be of considerable use and we
argue that it be required to cope with the complex issue
of stakeholder engagement.
PP:
Visualizing Stakeholder Influence - Two Australian
Examples. This paper illustrates the use of
the Stakeholder Circle
as a tool for measuring and visualizing stakeholder
influence drawing upon two case study examples. It is
exploratory in nature and the case studies used provide a
useful vehicle for reflection and sense making.
Development of the Stakeholder
Circle was based upon stakeholder and
project management theory and it extends our appreciation
of the potential impact that stakeholders may exert that
unearths vital risk management and customer relationship
implications for the project management profession. Using
a case study and action learning approach, this paper
draws upon emerging project management and wider strands
of management decision-making literature. The results of
the analysis showed significant differences in the
processes needed to manage the respective groups. The
project teams recognized they needed to adopt
significantly different strategies to achieve stakeholder
engagement, leading to stakeholder satisfaction and a
successful project. The tool was found by the case study
respondents to be useful and that it also complements and
enhances risk management approaches.The Stakeholder
Circle can be of considerable use and we
argue that it be required to cope with the complex issue
of stakeholder engagement.
PP: Influence, Stakeholder Mapping and Visualization. Stakeholder identification, management and engagement are recognized as key project management skills that requires both intuition and a strong capacity for analysis. Visualization tools for stakeholder management can be of great value. The development and use of two such tools are described. While they are both independently useful they could be effectively combined. This is a preprint of an article whose final and definitive form has been published in the Construction Management and Economics, June 2008 [copyright Taylor & Francis]