Location:
PMKI > People
Skills & Qualifications > Personal Ethics
& Sustainability.


- Personal Ethics
- Ethical Decision Making
- Professionalism
- Sustainability
- Green Project Management
- Green Building
- Useful External Web-links &
Resources.
Other related sections of the PMKI:
- Ethics and Culture in
organizations
- Competencies &
Interpersonal Skills
- Leadership & Motivation
- PM Qualifications
- Develop and manage the
project team
- The Evolution of Governance
& Ethics
Blg: The Evolution of Ethics. The evolution of ethical thinking from the Ancient Greeks to Post Modernism.
WP: Ethics and Leadership. A strong ethical framework is vital for personal success and underpins your ability to lead. Ideally this framework will be supported by the organization's governance structures.
Art: Ethical Leadership. The crucial role leaders play in establishing the ethical culture of their organizations - ethical standards are set at the top!
Blg: Practical Ethics. Blind trust in the ethical standards of others is dangerous. The role of ethical leaders is first to set the ethical standards, and then implement systems that require their followers to conform.
Blg: Practical Ethics 2. The ethical standards of an organization are set by the actions of its leaders (not what they say). What they do sets the ceiling and what they tolerate in others the floor.
Blg: Making Ethics Effective. The need for surveillance and enforcement to support ethical standards.
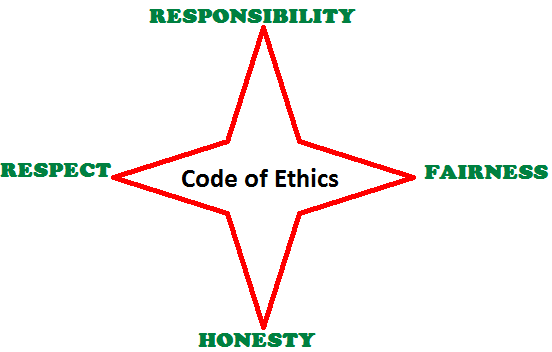 Download the PMI
Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct
Download the PMI
Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct
Download the ISO Code of Ethics and Conduct
See more on the evolution of
ethics.
 Every
decision you make has an ethical component. The PMI Ethical Decision-Making
Framework (EDMF) describes steps that
can be used to guide you through a process to make a
decision when confronted with an ethical dilemma. Download
the PMI Ethical Decision-Making Framework
Every
decision you make has an ethical component. The PMI Ethical Decision-Making
Framework (EDMF) describes steps that
can be used to guide you through a process to make a
decision when confronted with an ethical dilemma. Download
the PMI Ethical Decision-Making Framework
Blg: Tired workers lose their ethics. Tired people are more grumpy, absent minded and clumsy than normal and new research suggests that they are also more likely to cheat!
Art: The Problem with Paradox. Virtually every management system generates a series of paradox that cannot be removed because both of the factors that create the paradox are important, but at the same time contradict each other. This article discusses how to live with paradox.
Click through to see more on practical decision making.
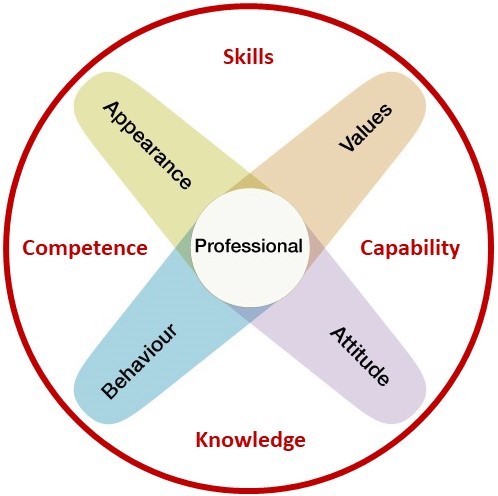 The
dimensions
of professionalism are:
The
dimensions
of professionalism are:
Blg: The Origins of Integrity. Integrity as we know it today stands for soundness of moral principle and character – uprightness – honesty; but there's more.
Art: Ethics, Integrity and Governance. The mutual interdependence between ethics, personal integrity, and the governance of organizations - does an organization have ethical responsibilities?
Blg: The moral underpinnings of good policy. The relationship between morals, ethics, values, principles and policies.
Art: Professional Project Management. What does professional project management look like? This article looks at the concept of a formal profession and what this means for project management.
Blg: The personal liability of Project Managers is increasing. Disputes are not restricted to business-vs-business, as this post demonstrates project managers can be held personally liable for loss and damage caused by their bad decisions.
Sustainability is a social goal focused on the ability
of people to co-exist on Earth over a very long time-span.
In business and policy contexts, it refers to the ability
to maintain or support a process continuously over time
while preventing the depletion of natural or physical
resources. This topic includes:
- Responsible project management
- Green project management
- Green building.
Art: Sustainable project management. Using the UN Sustainable Development Goals, and 'Green Project Management' to enhance your project's 'triple bottom line'.
Art: CSR, TBL, and Too Many Other Acronyms. This article looks at the relationship between ESG, CSR, TBL and a range of other concepts built around the need for organizations to act in ways that are socially and environmentally sustainable.
Blg: Who Gives a Crap about Sustainability? We do!. Small changes in daily actions can lead to big improvements in sustainability and save money.
ISO 14001:2015 is an international standard that defines the controls needed to reduce your organization’s environmental impact as a result of its operations. Certification to the standard is available. ISO 14001:2015 helps organization's manage their environmental impacts, ensure legal compliance, identify efficiencies, and reduce costs. To operate in a socially responsible manner and meet legal obligations it is important for an organization to identify the environmental aspects of its operations and manage the associated risks in areas such as environmental impacts, the use of natural resources, pollution of land and water, increase in carbon production, and destruction of natural habitats.
 P5
Standard for Sustainability in Business Practice, is
a framework set to transform how businesses integrate
sustainability into their operations. With elements
targeting ethical issues this latest take on the P5
Standard developed by GPM is poised to set new benchmarks
in corporate responsibility and ethical business conduct.
Including:
P5
Standard for Sustainability in Business Practice, is
a framework set to transform how businesses integrate
sustainability into their operations. With elements
targeting ethical issues this latest take on the P5
Standard developed by GPM is poised to set new benchmarks
in corporate responsibility and ethical business conduct.
Including:
- Five Lenses of Perspective: The P5 Standard
examines sustainability through five
comprehensive lenses, ensuring a holistic
approach.
- Eleven Categories: The standard includes four
categories under social, four under environmental, and
three under prosperity, providing a
balanced framework for assessing sustainability.
- 51 Sustainability Elements : With these elements,
the P5 Impact Assessment and Sustainability
Intervention Plan offer 255 ways to evaluate
sustainability, making it a robust tool for businesses.
Green Project Management (GPM) Global is dedicated to
making sustainability accessible. They offer the P5 Impact
Assessment and Sustainability Intervention Plan as free
resources alongside the standard. https://greenprojectmanagement.org/
The manifesto is a call for project professionals to expand their roles by advocating for beneficial change It aims to help facilitate conversations that value
While we recognize that projects programs and portfolios need to deliver outputs, outcomes and benefits, we believe that unless we all look after local communities, society and the natural world, projects will contribute to the destruction of humanity The signatories to this Manifesto are developing and applying ways of managing projects to realize social, environmental and economic value without preference.
10 Driving Principles
See more on the manifesto for responsible project
management at: https://www.responsiblepm.com/
The Green Project Management global movement has developed models for sustainability, training, and certification of individuals based on the following principles:
These principles are encapsulated in the GMP360 model:
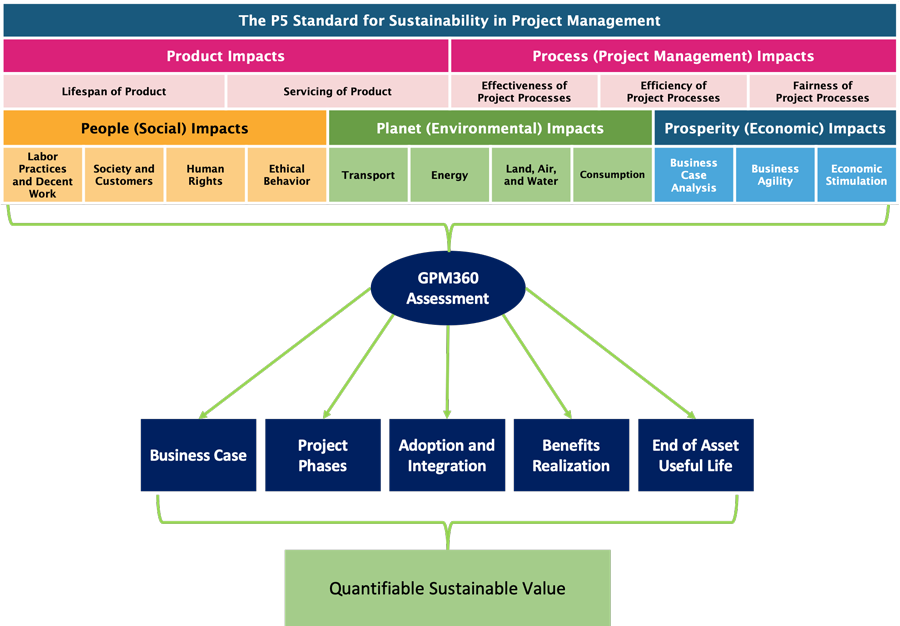
Download the GPM P5 Standard for Sustainability
in Project Management v3.0
Achieving a sustainable outcome requires people with the right skills, abilities, and attitudes. The GPM Sustainability Competence Standard 2.0 is a comprehensive guide to what individuals and organizations need to support sustainability and sustainability initiatives. It contains a detailed breakdown of the competences expected of sustainability professionals, from understanding the fundamentals of environmental stewardship to assessing the impacts of sustainability initiatives. This GPM standard also highlights the importance of ethical leadership, stakeholder collaboration and engagement, and the ability to inspire and drive change. Download the GPM Sustainability Competence Standard 2.0
Or click through to the GPM website for more information:
https://greenprojectmanagement.org/
The older GPM P5 Standard for Sustainability in
Project Management v2.0 can be downloaded for
historical reference.
Blg: Ethics and sustainability. Building ethics and sustainability into a project does not limit its success; in fact the reverse is often true. The disposal of millions of tones of excavated material from the Crossrail project has created a wildlife haven.
The built environment sector accounts for approximately 40% of process-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Of this 27% comes from building use (operations) and 13% from the construction industries including manufacture and transport of materials used in building roads, houses, etc. The good news is the industry has been working to reduce emissions and is having some success. Some of the organizations leading the change are:

ZERO is an independent industry group of construction professionals from a range of backgrounds. Their vision of the future is an industry that places great importance on carbon efficiency. An industry that continuously measures and manages carbon through all project stages, basing project decisions on CO2 emissions, not just cost, time, quality, and safety. Their mission is to reach a wide audience, and spark change on projects, within organizations, and across the whole industry.
ZERO members use their collective experience in practical solutions and project realities to work towards creating a net zero emissions construction industry. This is being achieved by collaborating to learn, share, and raise awareness of relevant topics to create content that is accessible and engaging and focused on original thinking and innovation.
Key initiatives:
The ZERO Playbook a free guide to decarbonise construction.
The ZERO Accredited Professional course builds upon the playbook and gives you 10 CPD points.
See more at: https://academy.zeroconstruct.com/
 The
World Green Building Council (WorldGBC) is the
largest and most influential local-regional-global action
network, leading the uptake of sustainable and
decarbonized built environments for everyone, everywhere.
The WorldGBC works with businesses, organizations and
governments to deliver on the ambitions of the Paris
Agreement and UN Global Goals for Sustainable Development.
The
World Green Building Council (WorldGBC) is the
largest and most influential local-regional-global action
network, leading the uptake of sustainable and
decarbonized built environments for everyone, everywhere.
The WorldGBC works with businesses, organizations and
governments to deliver on the ambitions of the Paris
Agreement and UN Global Goals for Sustainable Development.
Together, with the 75+ Green Building Councils which are
members of the WorldGBC global network, and industry
partners from all around the world, the WorldGBC are
driving systemic changes to:
- Address whole life carbon emissions of existing and new
buildings Enable resilient, healthy, equitable and
inclusive places,
- Secure regenerative, resource efficient and waste-free
infrastructure, and
- Develop and administer many of the world’s ratings
tools.
See more at: https://worldgbc.org/
 Architecture 2030 is another early initiative,
based in the USA. Over the last two decades, with modest
resources, it has achieved impressive shifts in outlook
and practice within the U.S. and global building sectors.
The organization works to create the initiatives necessary
to empower designers, policymakers, and educators to
facilitate systemic change and achieve a zero-carbon built
environment.
Architecture 2030 is another early initiative,
based in the USA. Over the last two decades, with modest
resources, it has achieved impressive shifts in outlook
and practice within the U.S. and global building sectors.
The organization works to create the initiatives necessary
to empower designers, policymakers, and educators to
facilitate systemic change and achieve a zero-carbon built
environment.
See more at: https://architecture2030.org/
Blg: Built to last. This post questions the approach to green ratings - should we be building for durability rather then short-term sustainability?
Blg: Every decision you make, every action you take has a carbon footprint. This post argues green building (and the measurement of carbon) needs to be re-framed to consider the whole building lifecycle rather then simply measuring the carbon embedded in the building process - most of the big savings are from design decisions focused on optimizing, operability, maintainability and durability.
Green building has been
included in the Sustainability section of this website (see above)
Click through to the
construction management section.
GPM Green Project Management: https://greenprojectmanagement.org
UN Sustainable Development website: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/
Manifesto for responsible project management: https://www.responsiblepm.com/